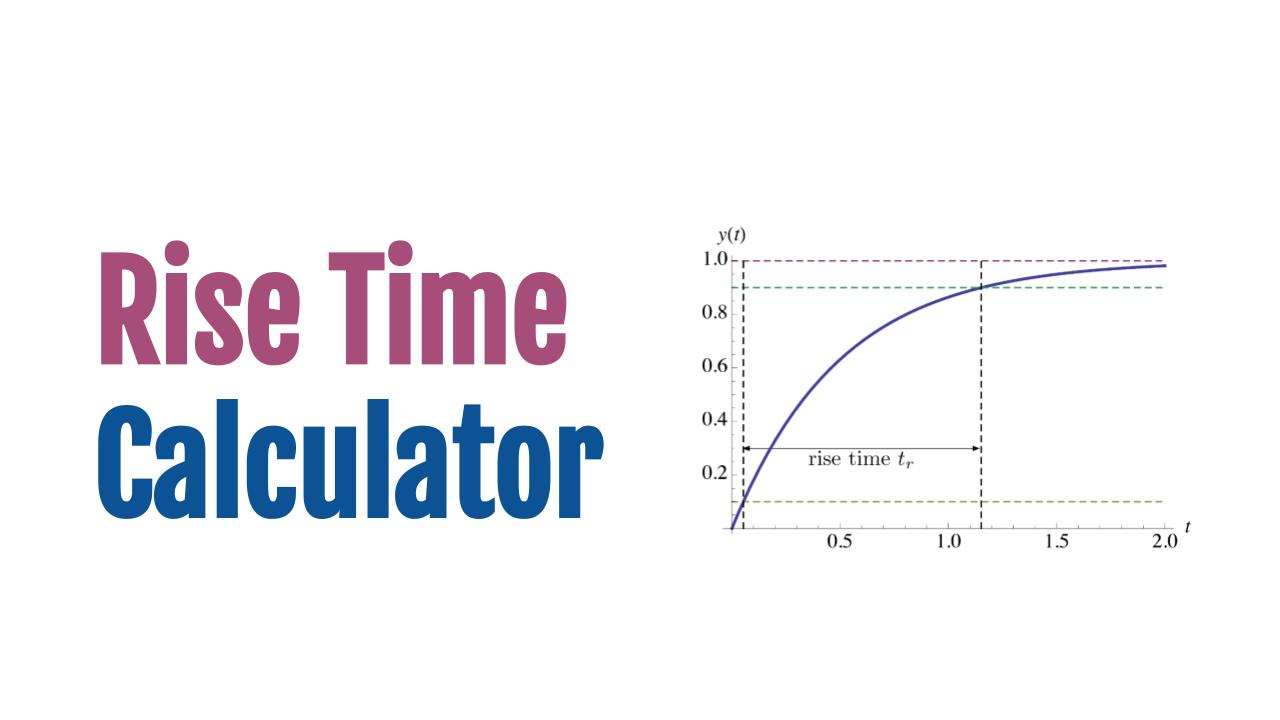
This tool computes the minimum Rise Time of a signal from its Bandwidth.
It’s useful if you want to find the fastest rise time that can be measured with an oscilloscope having a certain bandwidth specification.
Formula
Trise = 0.35 / BW
where
- Trise is the Rise Time in Nanoseconds (ns)
- BW is the Bandwidth in Gigahertz (GHz)
Background
What is Rise Time?
Rise time is the time it takes for a signal to transition from 10% to 90% of its full value. In practical terms, it tells us how fast a system can respond to sudden changes. A faster rise time means the signal can change more quickly.
What is Bandwidth?
Bandwidth refers to the range of frequencies that a system can transmit or process. Higher bandwidth allows the system to carry more information and respond to faster changes in signals, while lower bandwidth limits how quickly the signal can change without distortion.
Real-World Example
- If a communication system has a rise time of 1 microsecond, the bandwidth required would be approximately 350 kHz
This means the system needs 350 kHz bandwidth to accurately reproduce a signal with a rise time of 1 microsecond.
Why Does This Relationship Matter?
- Digital Circuits: Faster rise times are necessary for high-speed data transmission. To support faster signals, the circuit must have sufficient bandwidth.
- Communication Systems: In wireless communication, higher bandwidth is needed to maintain signal quality and ensure fast data rates.
- Oscilloscopes and Measurement Tools: When measuring fast signals, the instrument must have high bandwidth to capture the true shape of the signal.
Calculation Example
What is the rise time associated with a 50 MHz bandwidth?
The calculator is used to find Trise = 0.35 / 0.05 = 7 nanoseconds.
What is the rise time associated with a 250 MHz bandwidth?
Once again the calculator is used to find Trise = 0.35 / 0.25 = 1.4 nanoseconds.
As the bandwidth of the instrument increases, the rise time measurement capability is increased. In other words, with increasing bandwidth an oscilloscope can measure faster rise times.
What is Bandwidth?
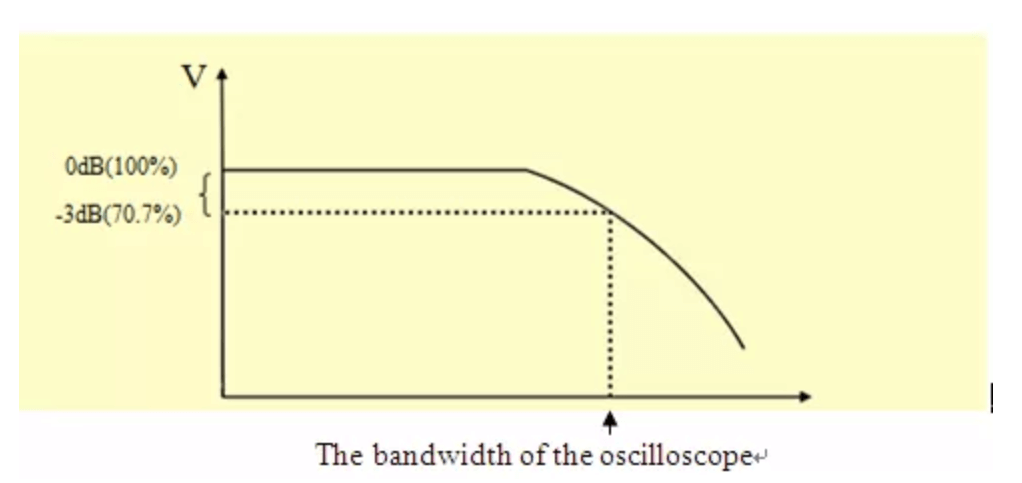
Within the context of an oscilloscope, bandwidth is the highest frequency of a sine wave that can be measured with at most a 3 dB error. In linear terms, the signal amplitude drops no more than 70.7% of its actual value as shown in the picture below. (Use -3 dB in the dB to normal value calculator)
Example Application
The calculator can be used to find the minimum rise time that can be measured by an oscilloscope considering its bandwidth specification.
An oscilloscope has a bandwidth of 200 MHz. The minimum rise time is therefore 1.75 ns. This oscilloscope will not be able to measure a rise time of 1 ns for example.
Related Calculators
- RC Rise time – calculates the Rise Time of a simple RC low pass filter network
- Square Wave Harmonics
References
[1] Bandwidth of a signal from its rise time: Rule of Thumb #1. In this post the author derives the relationship between rise time and bandwidth empirically.
[2] How do I determine what bandwidth of scope I require for my application? An application note that estimates a 2% measurement error when the five times rule is used.