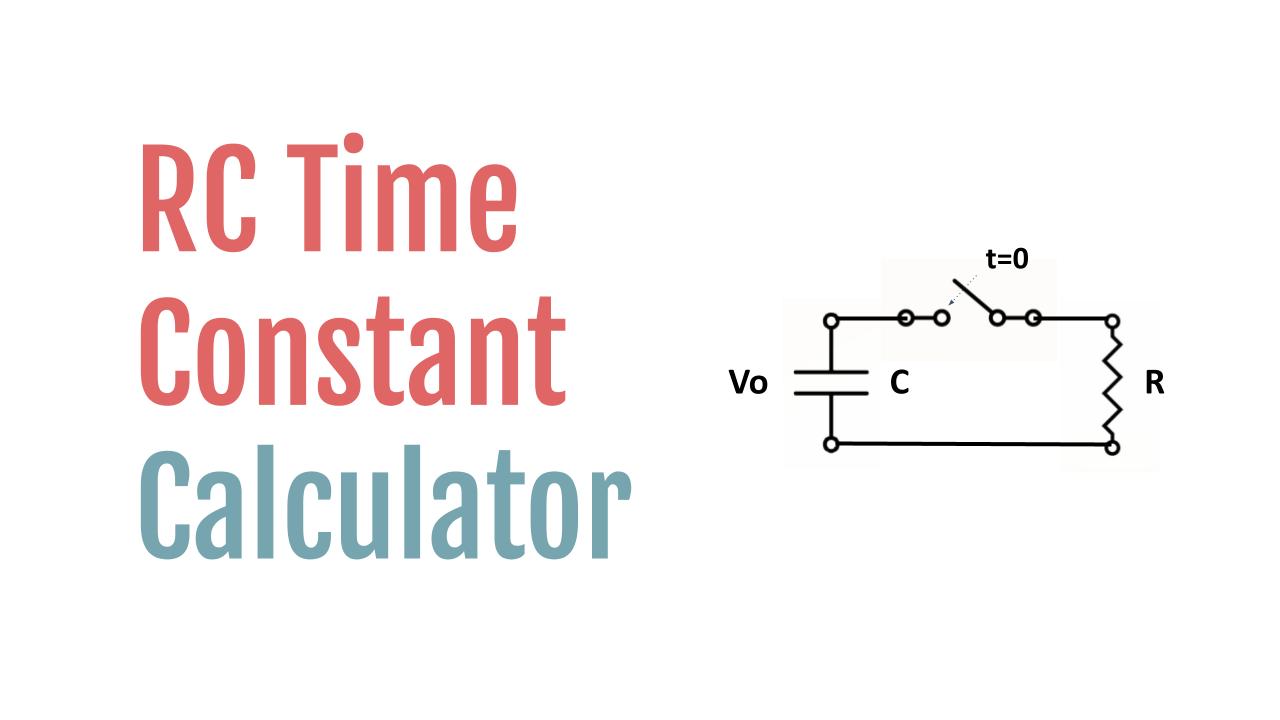
The RC time constant, represented as τ (tau), is a measure used in electrical engineering to quantify the time it takes for a capacitor, through a resistor, to charge to approximately 63.2% of the voltage supply or discharge to about 36.8% of its initial charge voltage.
Calculator
Enter
- Resistance R with units ohm (Ω)
- Capacitance C with units Farad (F)
Formula
τ = R*C
Where
- R is the resistance in ohm (Ω)
- C is the capacitance in Farad (F)
- τ is the time constant in seconds
Example Calculation
For a resistor value of 1 ohm and Capacitor value of 10 µF, the time constant is 10 µs.
Application
The significance of the RC time constant lies in its utility for predicting how quickly a circuit responds to a change in voltage.
For instance, in a charging capacitor scenario, the voltage across the capacitor at any time ( t ) can be calculated using the formula:
Vc = Vi (1-e-t/τ)
where,
- Vi = Input Voltage
- τ = time constant
- Vc = voltage at the capacitor at time t
time constant τ = RC, where R is resistance and C is capacitance.
Similarly, for a discharging capacitor, the voltage across it decreases over time following the exponential decay formula:
V = Vo*e−t/RC
The time constant time constant τ = RC, where R is resistance and C is capacitance. The time t is typically specified as a multiple of the time constant.
t = RC*Loge(Vo/V)
Related Posts
- RC Rise Time Calculator
- Capacitor discharge resistor calculator
- Cap discharge current calculator
- Capacitor Frequency Calculator