This tool converts from Wavelength in nm, um, mm, cm, m, inches or feet to Frequency in Hz, kHz, MHz, GHz.
Conversion Formula
Frequency f is given by the formula
f = c/λ
where, c is the speed of light and λ is the wavelength. As the wavelength increases the frequency decreases.
In a vacuum, the speed of light is c = 299,792,458 meters/second often approximated as 3 × 108 m/s. It is slower in other media such as in glass for instance where the speed is 200,000,000 meters/second. Change the value of c in the calculator above to calculate the frequency in this case.
For a fixed value of wavelength, as c increases, so does f.
The picture below shows the wavelength (λ) of a sine wave
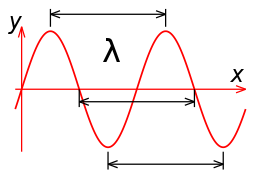
Background
The relation between frequency and wavelength is important as it helps understand the behavior of waves.
The wavelength is the distance between two consecutive points on a wave, whereas the frequency is the number of oscillations or cycles that occur within a given time period.
Frequency and wavelength are inversely proportional to each other. As the wavelength increases, the frequency decreases, and vice versa. For example, visible light has a higher frequency compared to radio waves, hence it has a shorter wavelength.
This relationship is governed by the equation v = λf, where v represents the wave speed or velocity, λ represents the wavelength, and f represents the frequency. The equation highlights that the wave speed is equal to the product of wavelength and frequency. Additionally, the amplitude of a wave is another significant factor that determines the number of times a wave oscillates within a given time.
Key Insights
- High Frequency = Short Wavelength
Waves with a higher frequency (e.g., gamma rays) have shorter wavelengths. This is why high-frequency waves are more energetic and capable of penetrating materials. - Low Frequency = Long Wavelength
Waves with a lower frequency (e.g., radio waves) have longer wavelengths. These waves are less energetic but can travel longer distances and diffract around obstacles.
Frequency and Wavelength in RF Engineering
Most radio engineers are used to referring to regions of the electromagnetic spectrum in terms frequency – for instance the Wi-Fi band is 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz.
The exception is when you get to lower frequencies in HF and VHF. At these bands, hobbyists and technologists refer to wavelength. For instance the 2 meter and 70 cm bands. It can be a little confusing sometimes. I developed this calculator to convert between the two.
Example Calculations
- 2m Wavelength is equivalent to approximately 150 MHz
- 10 mm is equal to a frequency of 30 GHz
